Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, organizations often need to move data between different database systems efficiently and reliably. One common scenario is exporting data from PostgreSQL to Snowflake, whether for analytics, data warehousing, or system migration purposes. Sling makes this process straightforward and efficient.
Sling is a modern data movement and transformation platform that simplifies database operations. It provides both a command-line interface (CLI) and a comprehensive platform for managing data workflows between various sources and destinations. When it comes to PostgreSQL to Snowflake migrations, Sling offers several key advantages:
- Efficient Data Transfer: Optimized for handling large datasets
- Schema Compatibility: Automatic handling of data type mappings
- Flexible Sync Options: Support for full refresh, incremental, and snapshot modes
- Data Validation: Built-in data integrity checks
In this guide, we’ll walk through the process of setting up Sling and using it to export data from PostgreSQL to Snowflake, complete with practical examples and best practices.
Getting Started with Sling CLI
Before we can start moving data, we need to install the Sling CLI. The installation process is straightforward and varies depending on your operating system.
Mac Installation
If you’re using a Mac, you can install Sling using Homebrew:
# Install using Homebrew
brew install slingdata-io/sling/sling
# Verify the installation
sling -h
Windows Installation
For Windows users, installation is available through Scoop:
# Add the Sling bucket
scoop bucket add sling https://github.com/slingdata-io/scoop-sling.git
# Install Sling
scoop install sling
# Verify the installation
sling -h
Linux Installation
On Linux systems, you can download and install Sling directly:
# Download the latest version
curl -LO 'https://github.com/slingdata-io/sling-cli/releases/latest/download/sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz'
# Extract and install
tar xf sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz
rm -f sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz
chmod +x sling
# Verify the installation
./sling -h
Once Sling is installed, you’ll have access to its powerful data movement capabilities through the command line interface.
Setting Up Database Connections
Before we can transfer data, we need to configure and test our connections to both PostgreSQL and Snowflake. Sling provides a simple way to manage database connections through the sling conns command.
PostgreSQL Connection Setup
Let’s start by setting up the PostgreSQL connection. You’ll need the following information:
- Host address
- Port number (default is 5432)
- Database name
- Username
- Password
Here’s how to set up the PostgreSQL connection:
# Set up PostgreSQL connection using connection string
sling conns set POSTGRES url="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database"
# Or set up using individual parameters
sling conns set POSTGRES type=postgres \
host=your-host \
user=your-user \
database=your-database \
password=your-password \
port=5432
Snowflake Connection Setup
For Snowflake, you’ll need:
- Account identifier (e.g., xy12345.us-east-1)
- Username
- Password
- Database name
- Warehouse (optional)
- Role (optional)
Here’s how to set up the Snowflake connection:
# Set up Snowflake connection using connection string
sling conns set SNOWFLAKE url="snowflake://user:password@account/database?warehouse=compute_wh&role=accountadmin"
# Or set up using individual parameters
sling conns set SNOWFLAKE type=snowflake \
account=your-account \
user=your-user \
password=your-password \
database=your-database \
warehouse=your-warehouse \
role=your-role
Testing the Connections
After setting up the connections, it’s important to test them to ensure they’re working correctly:
# Test PostgreSQL connection
sling conns test POSTGRES
# Test Snowflake connection
sling conns test SNOWFLAKE
If the connections are successful, you’ll see a success message. If there are any issues, Sling will provide detailed error messages to help you troubleshoot.
Listing Available Connections
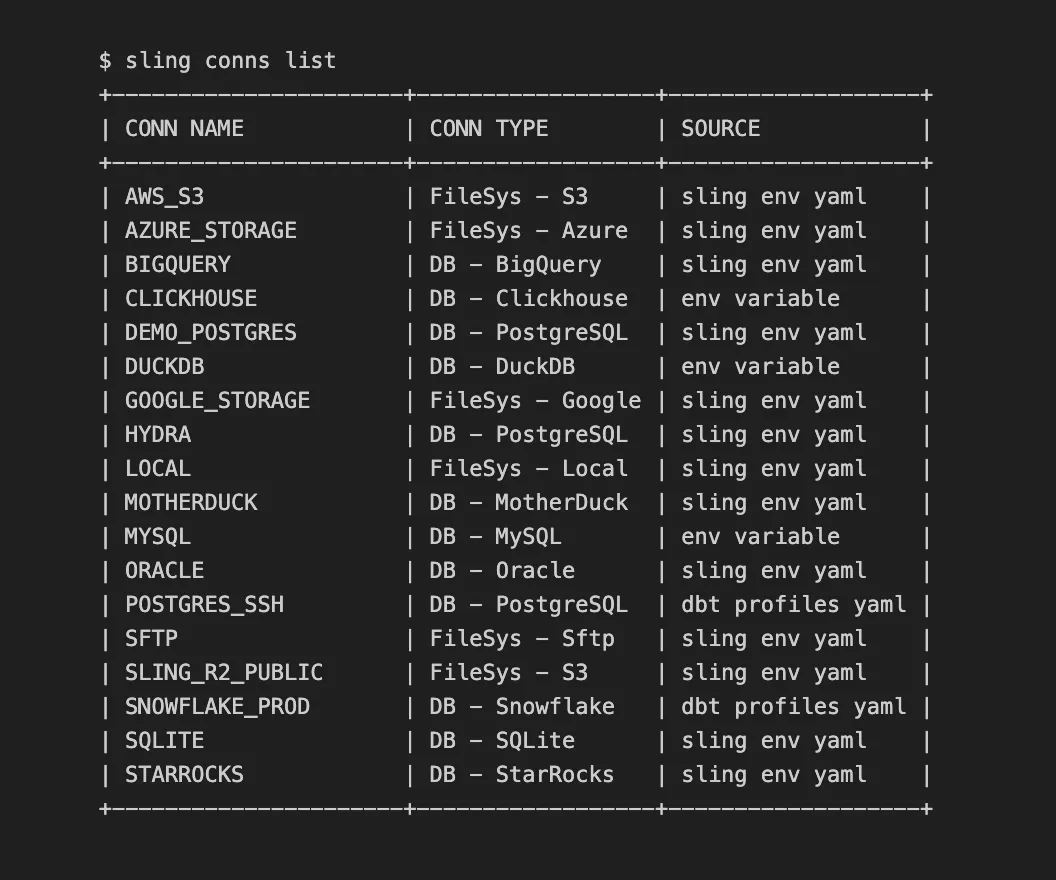
You can view all configured connections using:
sling conns list
This will display a table showing all your configured connections and their types:
Data Replication Examples
Now that we have our connections set up, let’s look at different ways to replicate data from PostgreSQL to Snowflake. While Sling supports both CLI flags and YAML configurations, using YAML files provides better organization and reusability for your data workflows.
Basic Table Replication
The simplest way to copy tables from PostgreSQL to Snowflake is using a basic YAML configuration with wildcards:
# basic-replication.yaml
source: postgres
target: snowflake
defaults:
mode: full-refresh
streams:
'public.*':
object: 'analytics.{stream_table}'
Run the replication using:
sling run -r basic-replication.yaml
This configuration will:
- Read all tables from the PostgreSQL
publicschema - Create corresponding tables in the Snowflake
ANALYTICSschema, maintaining the original table names - Copy all the data, maintaining the schema structure
Incremental Data Loading
For tables that are frequently updated, you can use incremental mode to only copy new or modified records:
# incremental-replication.yaml
source: postgres
target: snowflake
defaults:
mode: incremental
streams:
# Orders table with timestamp-based updates
public.orders:
object: analytics.orders
primary_key: order_id
update_key: last_modified_at
# Customer updates with multiple primary keys
public.customer_addresses:
object: analytics.customer_addresses
primary_key: [customer_id, address_id]
update_key: updated_at
# Products table with version control
public.products:
object: analytics.products
primary_key: product_id
update_key: version_number
Custom SQL Transformations
You can include custom SQL queries and transformations in your replication:
# transformed-replication.yaml
source: postgres
target: snowflake
defaults:
mode: full-refresh
streams:
# Simple column selection
public.users:
object: analytics.users_basic
sql: |
SELECT id, first_name, last_name, email
FROM public.users
WHERE is_active = true
# Complex transformation with joins
order_summary:
object: analytics.order_summary
sql: |
SELECT
o.order_id,
c.customer_name,
o.order_date,
SUM(oi.quantity * oi.unit_price) as total_amount,
COUNT(DISTINCT oi.product_id) as unique_products
FROM orders o
JOIN customers c ON o.customer_id = c.id
JOIN order_items oi ON o.order_id = oi.order_id
GROUP BY o.order_id, c.customer_name, o.order_date
Advanced Configuration Options
Sling provides many advanced options for fine-tuning your replications:
# advanced-replication.yaml
source: postgres
target: snowflake
defaults:
mode: full-refresh
# Global source options
source_options:
empty_as_null: true
# Global target options
target_options:
table_ddl: |
create table {stream_table} (
{col_types},
loaded_at timestamp_ntz default current_timestamp()
)
streams:
# Table with custom column mapping
public.legacy_table:
object: analytics.modern_table
columns:
customer_id: string(50) # cast to string with max length of 50
# Table with incremental mode
public.large_events:
object: analytics.events
mode: incremental
primary_key: [event_id]
update_key: event_timestamp
# Table with custom transformations
public.transactions:
object: analytics.transactions
transforms:
number: [ empty_as_null ]
You can run any of these configurations using:
sling run -r <config-file.yaml>
For visual configuration and management of your replications, you can use the Sling Platform’s editor:
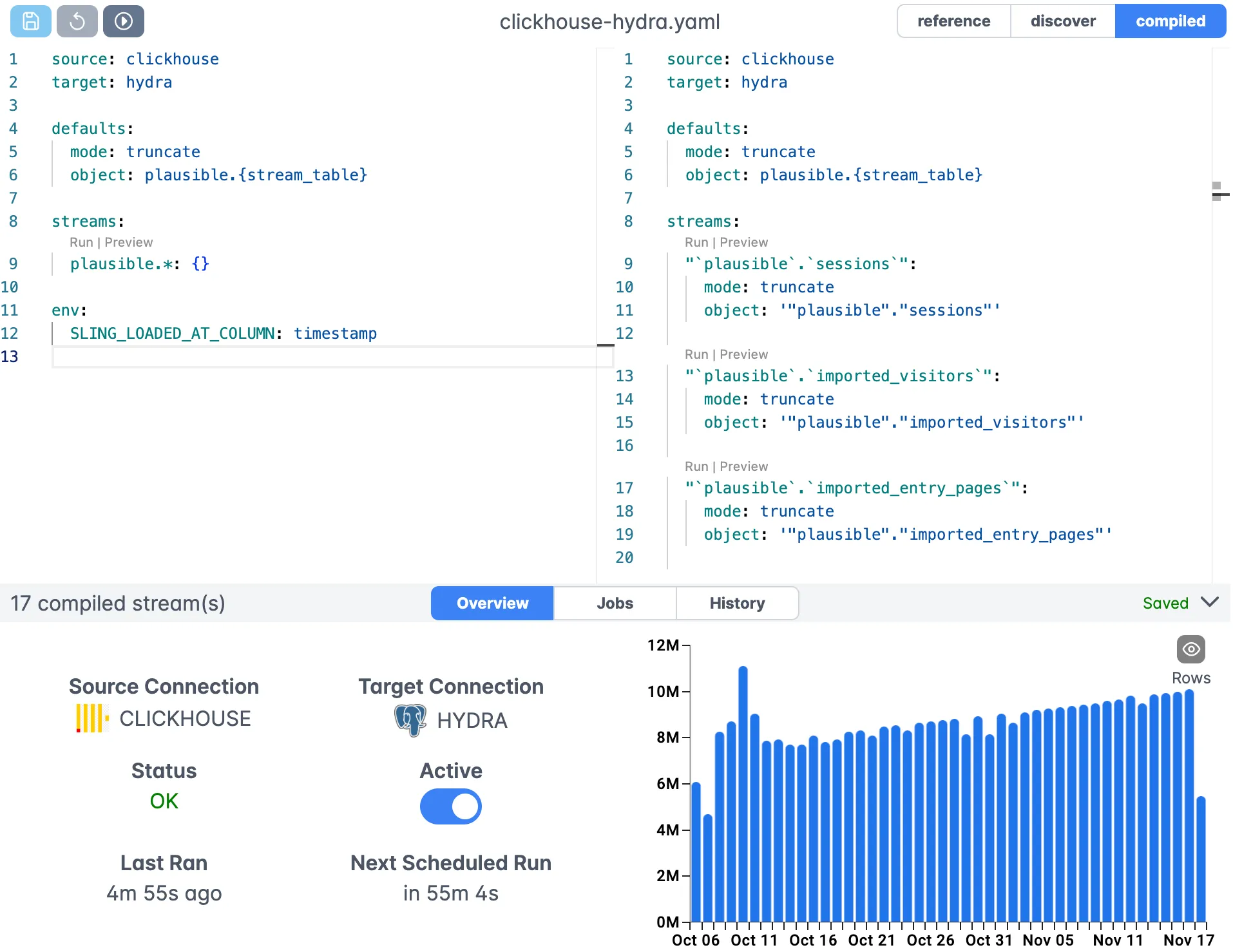
Conclusion
Sling provides a powerful and flexible solution for exporting data from PostgreSQL to Snowflake. Its key features include:
- Simple installation and configuration
- Support for various replication modes
- Advanced options for performance tuning
- Comprehensive CLI and platform interfaces
Whether you’re performing a one-time migration or setting up ongoing data synchronization, Sling’s capabilities make it an excellent choice for database operations. The tool’s ability to handle both simple and complex scenarios, combined with its user-friendly interface, makes it an invaluable asset for data engineers and analysts.
Next Steps
To further explore Sling’s capabilities, consider:
- Exploring the Sling Platform UI for visual workflow management
- Setting up automated replications using cron jobs or orchestration tools
- Joining the Sling community on Discord for support and best practices
- Checking out the documentation for advanced features
For additional support or to report issues, visit the GitHub repository or reach out to the support team at [email protected].



