Introduction
Moving data from SFTP servers to Snowflake has traditionally been a complex process requiring multiple tools and custom scripts. Organizations often struggle with challenges such as:
- Setting up and maintaining secure SFTP connections
- Handling CSV file formats and data type mappings
- Managing incremental loads and data transformations
- Ensuring reliable and scalable data transfers
- Monitoring and troubleshooting data pipelines
Sling simplifies this entire process by providing a unified, efficient solution for transferring data from SFTP servers to Snowflake. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through how to set up and use Sling for this specific use case, covering both command-line operations and YAML-based configurations.
Let’s dive into how you can streamline your SFTP to Snowflake data pipeline using Sling.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following:
- Sling CLI Installation
You can install Sling using various methods depending on your operating system:
# Install using Homebrew (macOS)
brew install slingdata-io/sling/sling
# Install using curl (Linux)
curl -LO 'https://github.com/slingdata-io/sling-cli/releases/latest/download/sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz' \
&& tar xf sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz \
&& rm -f sling_linux_amd64.tar.gz \
&& chmod +x sling
# Install using Scoop (Windows)
scoop bucket add sling https://github.com/slingdata-io/scoop-sling.git
scoop install sling
# Install using Python pip
pip install sling
Verify the installation by running:
# Check Sling version
sling --version
SFTP Server Requirements
- Host address and port (default is 22)
- Username and password or SSH private key
- Path to the CSV files you want to transfer
- Proper read permissions on the SFTP server
Snowflake Requirements
- Account identifier (e.g.,
xy12345.us-east-1) - Username and password
- Database name and schema
- Role with appropriate privileges
- Warehouse for processing
- Account identifier (e.g.,
CSV File Considerations
- Consistent file format and structure
- Well-defined column names and data types
- UTF-8 encoding recommended
- Proper delimiter and quote characters
Setting Up Connections
Before we can transfer data, we need to configure both our SFTP and Snowflake connections in Sling. Let’s set up each connection step by step.
SFTP Connection Setup
There are several ways to configure your SFTP connection in Sling:
- Using
sling conns setCommand
# Basic authentication with password
sling conns set MY_SFTP type=sftp host=sftp.example.com user=myuser password=mypassword port=22
# Using SSH private key
sling conns set MY_SFTP type=sftp host=sftp.example.com user=myuser private_key=/path/to/private_key port=22
- Using Environment Variables
# Using JSON/YAML format
export MY_SFTP='{type: sftp, host: sftp.example.com, user: myuser, password: mypassword, port: 22}'
- Using Sling Environment YAML
Create or edit ~/.sling/env.yaml:
connections:
MY_SFTP:
type: sftp
host: sftp.example.com
user: myuser
port: 22
password: mypassword
# Or use private key authentication
# private_key: /path/to/private_key
Snowflake Connection Setup
Similarly, let’s configure the Snowflake connection:
- Using
sling conns setCommand
# Basic configuration
sling conns set SNOWFLAKE type=snowflake account=xy12345.us-east-1 user=myuser password=mypassword database=mydb role=myrole warehouse=mywarehouse
# Using connection URL
sling conns set SNOWFLAKE url="snowflake://myuser:[email protected]/mydb?warehouse=mywarehouse&role=myrole"
- Using Environment Variables
# Using connection URL format
export SNOWFLAKE='snowflake://myuser:[email protected]/mydb?warehouse=mywarehouse&role=myrole'
- Using Sling Environment YAML
Add to your ~/.sling/env.yaml:
connections:
SNOWFLAKE:
type: snowflake
account: xy12345.us-east-1
user: myuser
password: mypassword
database: mydb
schema: public
role: myrole
warehouse: mywarehouse
Testing Connections
After setting up your connections, it’s important to verify they work correctly:
# Test SFTP connection
sling conns test MY_SFTP
# Test Snowflake connection
sling conns test SNOWFLAKE
# List available connections
sling conns list
These tests ensure that Sling can successfully connect to both your SFTP server and Snowflake instance before attempting any data transfers.
Data Transfer Methods
Sling provides two main approaches for transferring data from SFTP to Snowflake: using CLI flags for quick operations and using YAML configurations for more complex, repeatable workflows.
Using CLI Flags
The CLI approach is perfect for quick, one-off transfers or when you’re testing your setup:
- Basic Transfer
# Transfer a single CSV file
sling run --src-conn MY_SFTP --src-stream '/path/to/data.csv' \
--tgt-conn SNOWFLAKE --tgt-object 'public.my_table' \
--mode full-refresh
# Transfer multiple CSV files from a directory
sling run --src-conn MY_SFTP --src-stream '/path/to/csv_folder/*.csv' \
--tgt-conn SNOWFLAKE --tgt-object 'public.{stream_file_name}' \
--mode full-refresh
- Advanced Transfer with Options
# Transfer with column mapping and transformations
sling run --src-conn MY_SFTP --src-stream '/path/to/data.csv' \
--tgt-conn SNOWFLAKE --tgt-object 'public.my_table' \
--mode full-refresh \
--columns '{ "id": "integer", "name": "string", "created_at": "timestamp" }' \
--transforms '[remove_accents]' \
--src-options '{ "empty_as_null": true, "datetime_format": "YYYY-MM-DD" }' \
--tgt-options '{ "column_casing": "snake", "add_new_columns": true }'
Using Replication YAML
For more complex scenarios or production workflows, using a YAML configuration file provides better maintainability and version control:
- Basic Replication Configuration
Create a file named sftp_to_snowflake.yaml:
source: MY_SFTP
target: SNOWFLAKE
defaults:
mode: full-refresh
streams:
'/path/to/customers.csv':
object: public.customers
columns:
customer_id: integer
name: string
email: string(50)
created_at: timestamp
'/path/to/orders.csv':
object: public.orders
columns:
order_id: integer
customer_id: integer
order_date: timestamp
total_amount: decimal
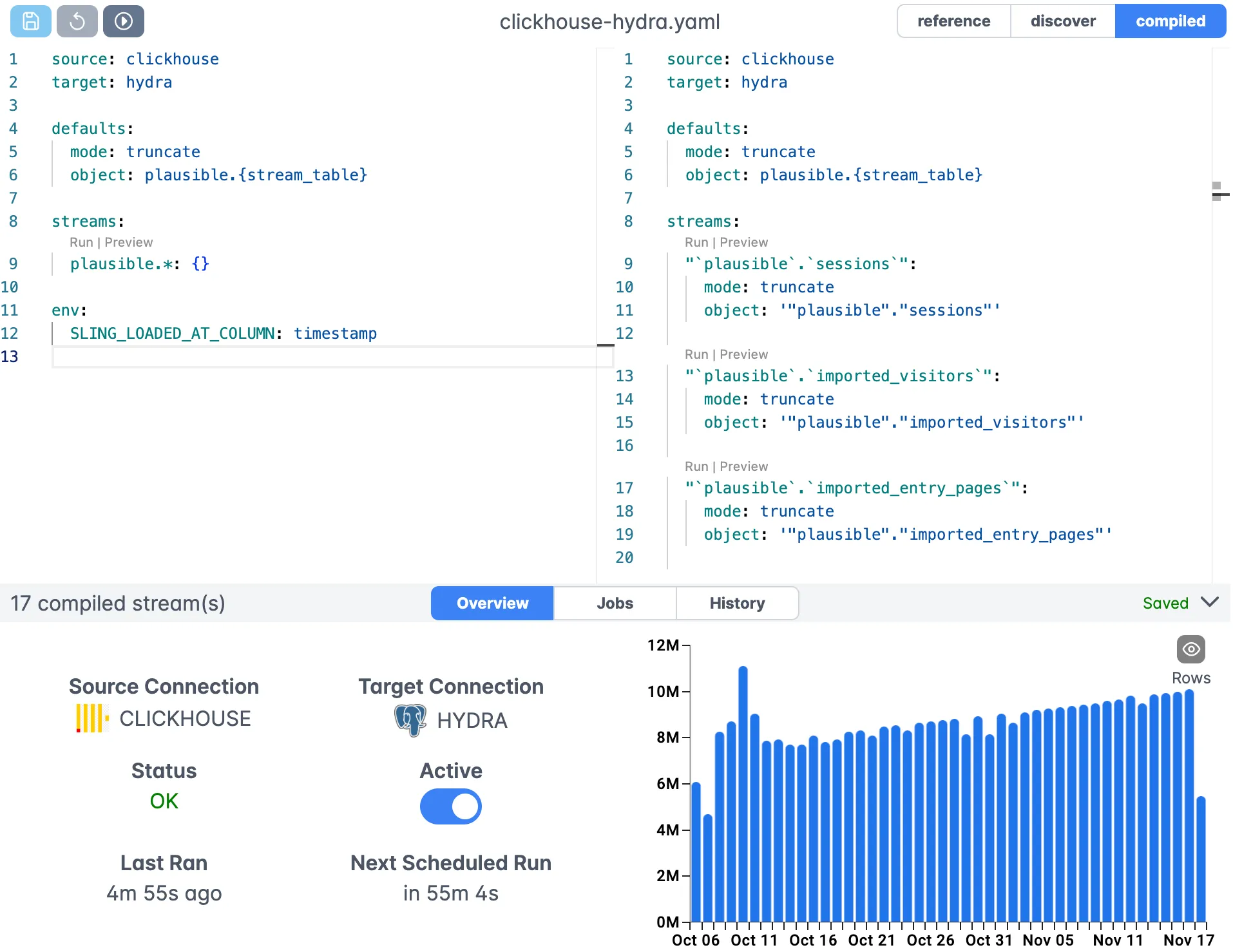
- Advanced Replication Configuration
Here’s a more sophisticated configuration with multiple streams, transformations, and options:
source: MY_SFTP
target: SNOWFLAKE
defaults:
mode: full-refresh
primary_key: [id]
source_options:
empty_as_null: true
datetime_format: "YYYY-MM-DD"
target_options:
column_casing: snake
add_new_columns: true
streams:
'/path/to/customers/*.csv':
mode: truncate
object: public.customers
columns:
id: integer
name: string
email: string
created_at: timestamp
transforms:
- remove_accents
- trim
source_options:
delimiter: "|"
'/path/to/orders/*.csv':
object: public.orders_{stream_table}
mode: incremental
columns:
order_id: integer
customer_id: integer
order_date: timestamp
total_amount: decimal
update_key: order_date
To run the replication:
# Run the replication configuration
sling run -r sftp_to_snowflake.yaml
Runtime Variables
Sling supports runtime variables that can be used in your YAML configurations for dynamic paths and table names:
{stream_file_name}: The name of the current file being processed{stream_table}: The table name derived from the file name{stream_schema}: The schema name if specified in the path
These variables are particularly useful when dealing with multiple files or when you want to maintain a consistent naming convention between your source files and target tables.
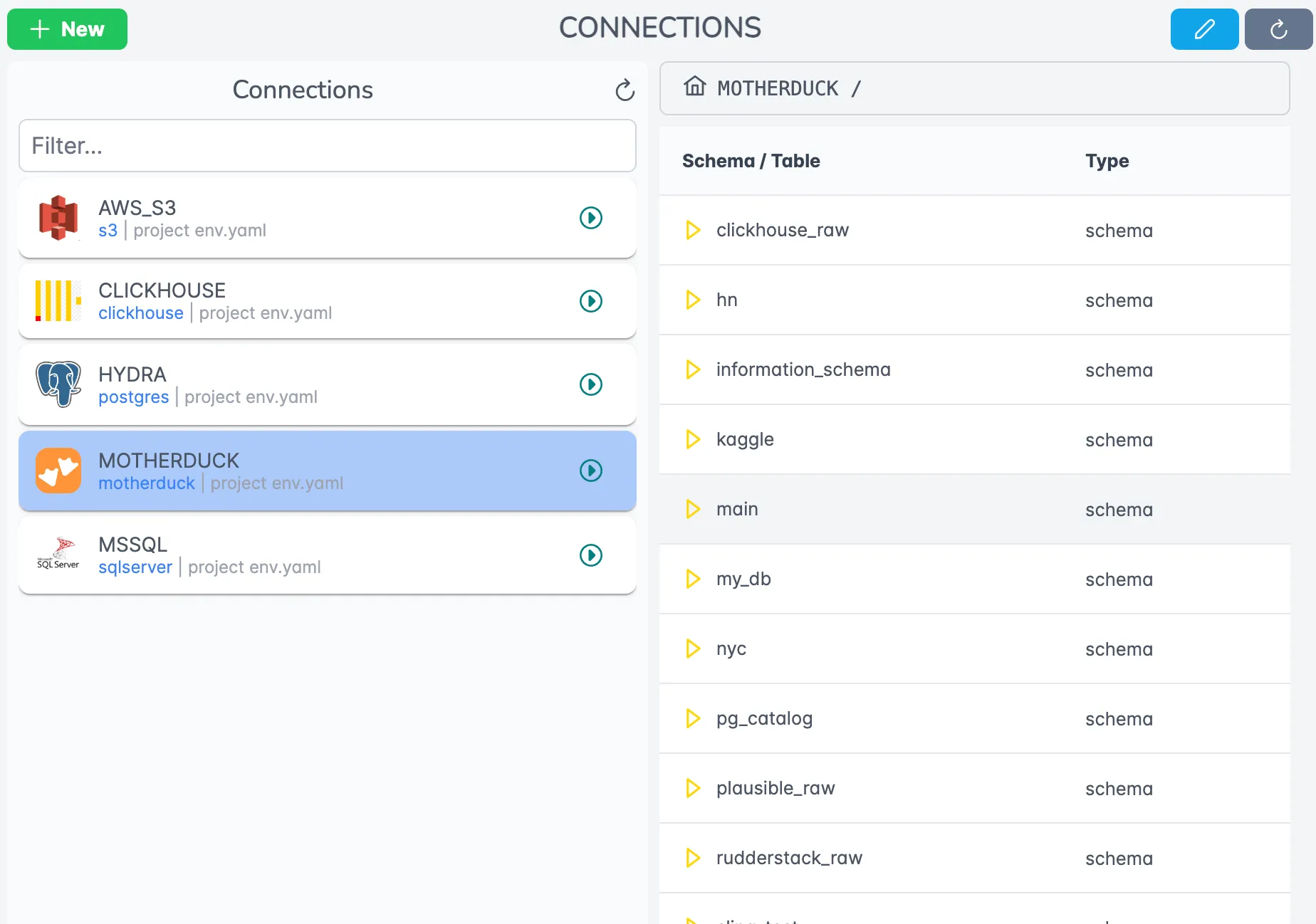
Sling Platform Overview
While the CLI is powerful for local development and testing, the Sling Platform provides a comprehensive web-based interface for managing your data operations at scale. Here are the key components:
Platform Components
Connection Management
- Centralized credential storage
- Connection testing and validation
- Role-based access control
- Support for multiple environments
Visual Editor
- YAML configuration editor with syntax highlighting
- Real-time validation
- Template library
- Version control integration
Job Management
- Scheduling and orchestration
- Dependency management
- Error handling and retries
- Monitoring and alerting
Agents
- Distributed execution
- Secure access to data sources
- Resource management
- Auto-scaling capabilities
Platform Interface
The Sling Platform provides an intuitive interface for managing your data operations:
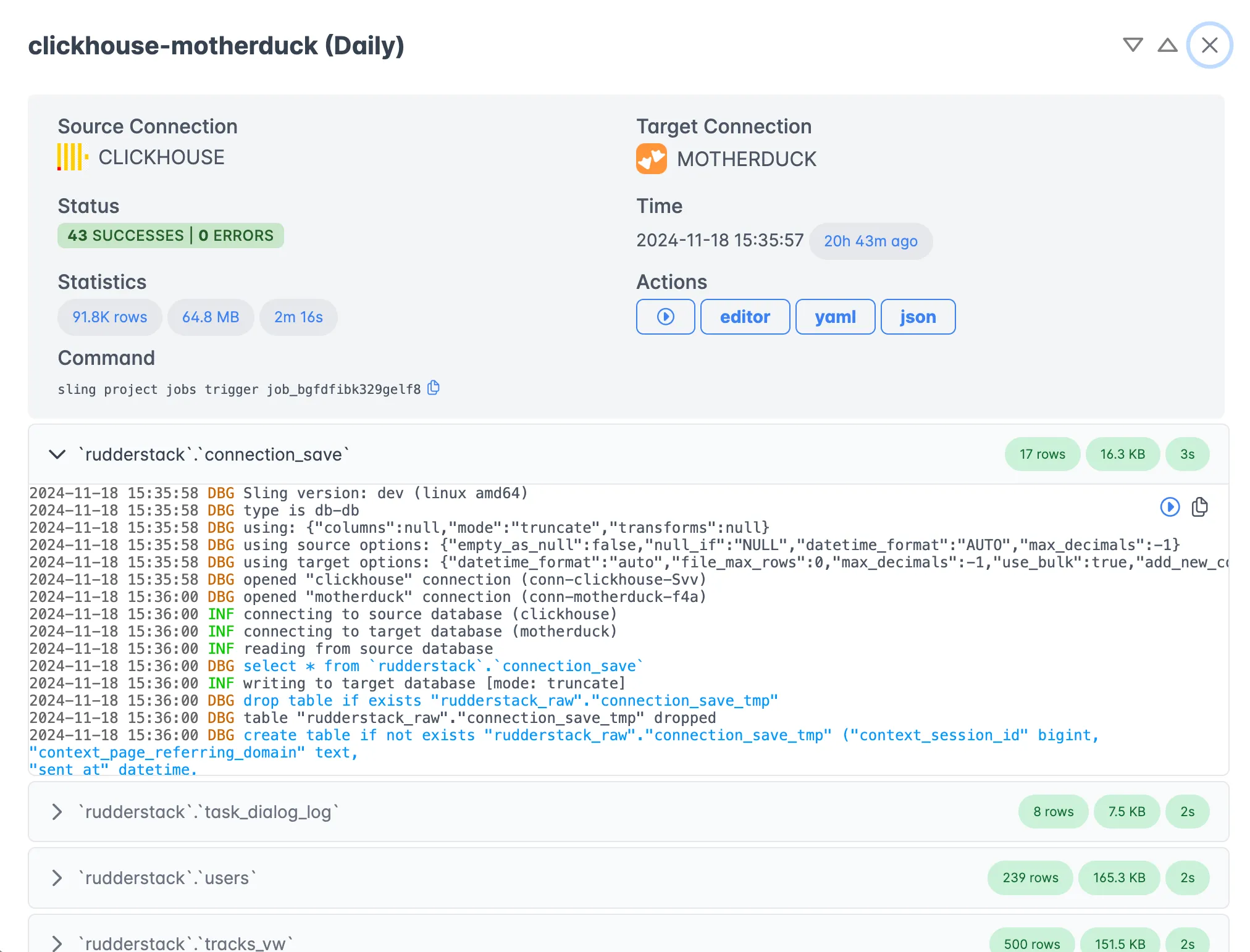
Key features include:
- Real-time job monitoring
- Detailed execution logs
- Performance metrics
- Error tracking and debugging tools
Agent Management
Agents are the workers that execute your data operations:
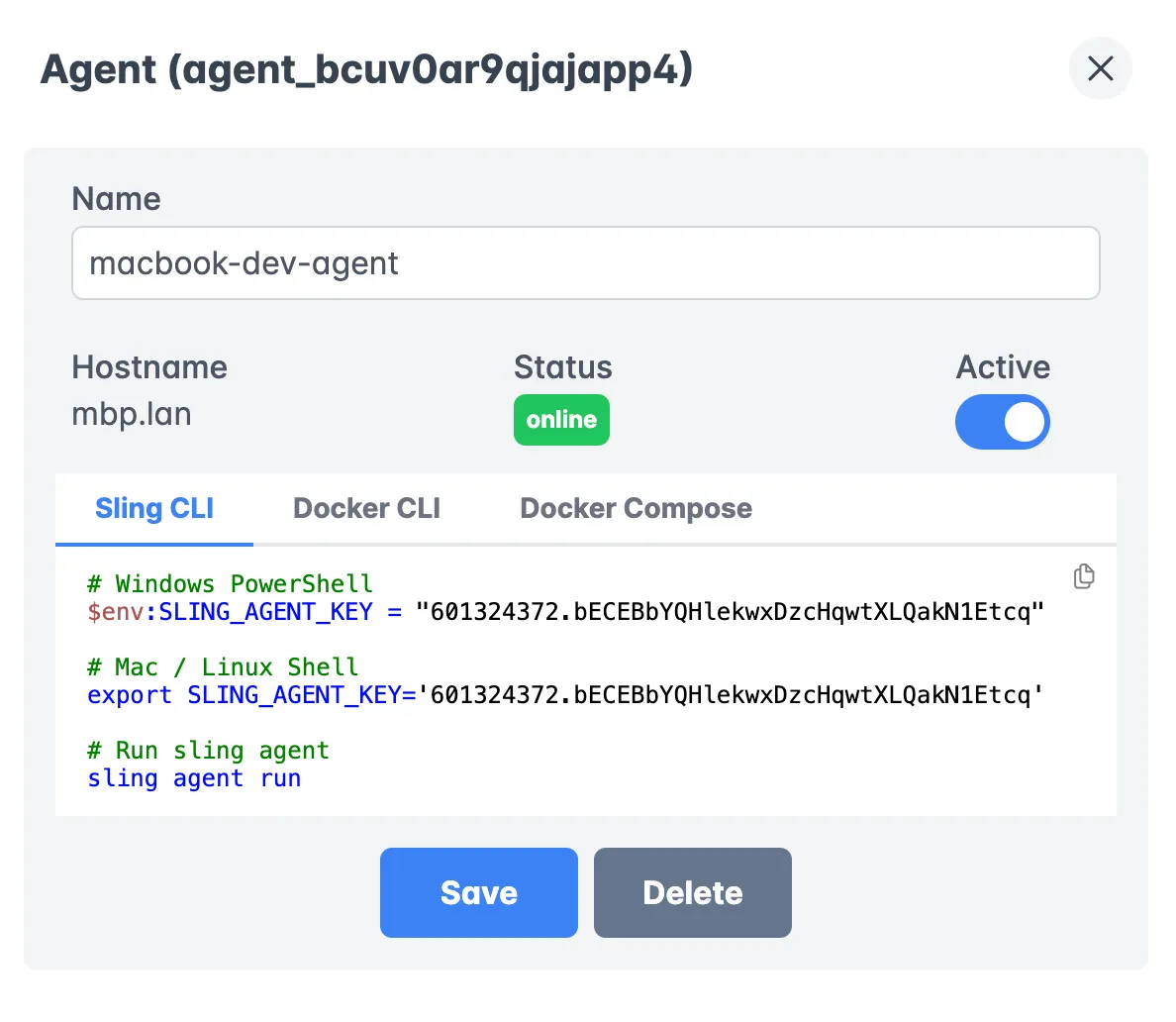
Benefits of using agents:
- Run in your own infrastructure
- Secure access to your data sources
- Support for both development and production environments
- Automatic updates and maintenance
Job History and Monitoring
Track all your data operations with comprehensive history and monitoring:
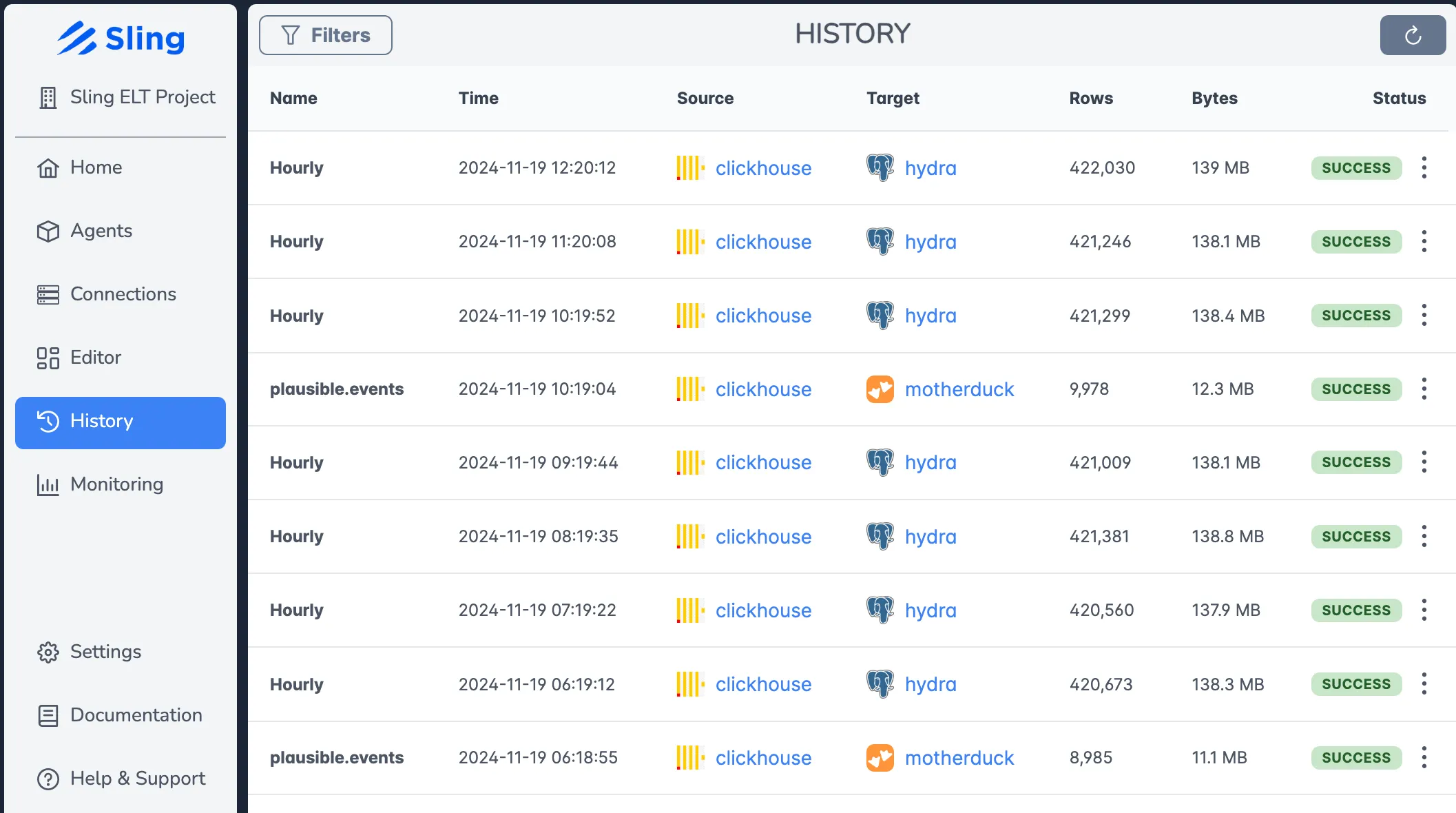
Features include:
- Historical execution data
- Success/failure tracking
- Performance trends
- Resource utilization metrics
Getting Started
Ready to streamline your SFTP to Snowflake data pipeline with Sling? Here’s how to get started:
Install Sling CLI
- Follow the installation instructions for your operating system
- Verify the installation with
sling --version
Set Up Your Environment
- Configure your connections using the environment guide
- Test your connections with
sling conns test
Create Your First Replication
- Start with a simple CLI command to test the transfer
- Create a replication YAML file for more complex workflows
- Learn about replication modes and options
Explore Advanced Features
- Check out source options for file handling
- Learn about target options for Snowflake optimization
- Understand runtime variables for dynamic configurations
Consider the Sling Platform
- Sign up at platform.slingdata.io
- Follow the platform getting started guide
- Deploy agents in your infrastructure
Additional Resources
- File to Database Examples
- Database to Database Examples
- Database to File Examples
- SFTP Connection Guide
- Snowflake Connection Guide
Community and Support
- Join our Discord community
- Report issues on GitHub
- Contact support at [email protected]
Start simplifying your data operations today with Sling!



